How to generate a new E-way bill for GST invoice on the e-way bill portal for transportation of goods from one place to another place.
As a new or old GST taxpayer, we need to know how to generate a new E-way bill which is highly demanded in the case of the supply of goods within the state or outside of the state.
Before the generation of a new E-way bill for GST invoice, you need to know some important words which are these
Contents of this post
Words need to know in the case of generating a new e-way bill
1-Supply type
- Outward supply/ sales
Outward Supply in relation to a person, shall mean the supply of goods or services, whether, by sale, transfer, barter, exchange, license, rental, lease or disposal or any other means made or agreed to be made by such person in the course or furtherance of business.
Table showing options available to choose for outward supply/ sales
| Sub-Type for outward supply | Document Type | To GSTIN (bill to) |
| Supply | Tax Invoice | Other GSTIN/URP |
| Bill of Supply | Other GSTIN/URP | |
| Export | Tax Invoice | URP |
| Bill of Supply | URP | |
| Job Work | Delivery Challan | Other GSTIN/URP |
| SKD/CKD/LOTS | Tax Invoice | Other GSTIN/URP |
| Bill of Supply | Other GSTIN/URP | |
| Delivery Challan | Other GSTIN/URP | |
| Recipient not known | Delivery Challan | Self |
| Other | Self | |
| For own use | Delivery Challan | Self |
| Exhibition or fairs | Delivery Challan | Self |
| Lines Sales | Delivery Challan | Self |
| Others | Delivery Challan | Self /URP/GSTIN |
| Other | Self /URP/GSTIN |
- Inward supply/ purchase
Inward supply literally means receiving goods or services or both. In this write-up, all aspects related to Inward supply are covered.
Table showing options available to choose for Inward supply/purchase
| Sub-Type for Inward supply | Document Type | From GSTIN (bill from) |
| Supply | Tax Invoice | Other GSTIN/URP |
| Bill of Supply | Other GSTIN/URP | |
| Import | Bill of Entry | URP |
| Job Work Return | Delivery Challan | Other GSTIN/URP |
| SKD/CKD/LOTS | Tax Invoice | Other GSTIN/URP |
| Bill of Supply | Other GSTIN/URP | |
| Delivery Challan | Other GSTIN/URP | |
| Bill of Entry | URP | |
| Sales Return | Delivery Challan | Other GSTIN/URP |
| Other | Self | |
| For own use | Delivery Challan | Self |
| Exhibition or fairs | Delivery Challan | Self |
| Others | Delivery Challan | Self /URP/GSTIN |
| Other | Self /URP/GSTIN |
2-Subtype for Outward supply/ sales
- Supply
This one is usable for the regular sale transactions, where the sale has taken place based on a Tax Invoice or Bill of Supply.
- Export
This option is used for the export transactions, where sale/export has taken place based on a Tax Invoice or Bill of Supply.
- Job work
This is used when the goods are moved for job work with Delivery Challan.
- SKD/CKD/LOTS
This is used when the goods are moved in completely or semi-knocked down condition or in lots. Under this condition, the taxpayer will move the parts of the goods along with the ‘Delivery Challan’ and copy of the ‘Tax Invoice’ and last consignment with ‘Delivery Challan’ and original Invoice.
- For own use
This is used when the goods are moved between the business places of the taxpayers. Generally, it is moved with Delivery Challan.
- Line sales
The line sales are useful when the goods are taken out from the premises of the taxpayers for the sales at the doorsteps of the clients.
The goods are taken out with the Delivery Challan and whenever the sales are made to the clients, the Taxable Invoice or Bill of Supply is issued to the amount of the sale taken place.
- Recipient not known
This is used when the goods are taken out from the premises of the taxpayers for the sales at the doorsteps of the clients. The goods are taken out with the Delivery Challan.
- Exhibitions or Fairs
This is used when the goods are taken out from the premises of the taxpayers to the premises of the Exhibitions or Fairs. The goods are taken out with the Delivery Challan.
- Other
Other is an option when the goods are taken on another type of supply. It is necessary for the taxpayers to specify the sub-supply type.
3-Subtype for Inward supply/ purchase
- Supply
This is used for the regular purchase transactions, where the purchase has taken place based on a Tax Invoice or Bill of Supply.
- Import
The Import is used for the import transactions, where purchase/import has taken place based on the Bill of Entry.
- SKD/CKD/Lots
This is used when the goods are purchased and moved in completely or semi-knocked down condition or in lots. Under this condition, the taxpayer will move the parts of the goods along with the ‘Delivery Challan’ and copy of the ‘Tax Invoice or Bill of Entry’ and last consignment with ‘Delivery Challan’ and original Invoice/Bill of Entry.
- Job work returns
This is used when the goods are moved for job work with Delivery Challan.
- Sales returns
This option is used when the goods are brought back from the client premises because of the rejection of the goods or not being ready to accept the goods.
- For own use
This is used when the goods are moved between the business places of the taxpayers. Generally, it is moved with ‘Delivery Challan’
- Exhibitions or Fairs
This is used when the goods are taken out from the premises of the taxpayers to the premises of the Exhibitions or Fairs. The goods are taken out with the ‘Delivery Challan’
- Others
Other is used when the goods are taken on another type of supply. It is necessary for the taxpayers to specify the sub-supply type.
4-Document Types
- Tax invoice
A tax invoice is a document issued by a registered dealer to the purchaser, showing the details of tax payable.
- Bill of supply
In some cases, the registered dealer cannot charge any tax on the invoice then the dealer has to issue a Bill of supply. And the dealer can not recover the tax amount. for example- Composition Dealer, Exporter, Exempted goods supplier.
5-Document No
It is a serial number that is mentioned in the GST invoice and is called to be an invoice number. And it should not exceed 16 characters.
6-Document Date
The invoice date is the date of the documents issued by the supplier to the recipient to clarify their obligations.
7-Transaction Type
- Regular
This type is a regular or normal transaction, where billing and goods movement is happening between two parties-consignor and consignee.
- Bill to – Ship to
In this type of transaction, three parties have involvement. Billing takes place between consignor and consignee, but the goods move from consignor to the third party place as per the request of the consignee.
- Bill from – Dispatch from
In this type of transaction also, three parties are involved. Billing takes place between consignor and consignee, but the goods are moved from the third party place to the consignee.
- And the combination of Bill to – Ship to and Bill from – Dispatch from
In this case, the combination of the above two transactions involves four parties. Billing takes place between consignor and consignee, but the goods are moved by the consignor from the third party place to the fourth party place as per the request of the consignee.
8-GSTIN Number
If the billing takes place between two registered dealers then the GSTIN No is required to mention in the E-way bill and GSTIN NO is required to issue an E-way bill online.
9-HSN Code
HSN Code is mandatory for generating an E-way bill online and it is the code for the identification of item
10-Cess
Cess is a type of charge on certain types of goods and you must pay it in addition to any required GST. This cess applies to interstate sales, intrastate sales, and imports. It does not apply to exports.
The government will collect, then distribute the cess to states to help them meet minimum revenue levels. This ensures that manufacturing-heavy states have enough money to operate.
11-Transport ID
This is the ID provided to the transporter when he gets his registration on the E-way bill portal if he is unregistered and if he is registered under the GST registration act.
Further, his GSTIN no is transport id which will use the consignor and consignee.
12-Vehicle Type
- Regular
In this case, the Regular type needs normal cargo.
- Over dimensional cargo
If a truck with a loading platform length of 20 feet is loaded with cargo like TMT bars of length 22 feet, then the TMT bars qualify as Over-Dimension Cargo. If the same TMT bars were loaded on a vehicle with a platform length of 22+ feet, it would have been classified as Normal Cargo rather than ODC. An extra validity period has been provided for Over Dimensional Cargo (ODC).
13-Vehicle No Format
This is the vehicle no format that will be acceptable to generate an e-way bill
AB121234, AB12A1234, AB12AB1234, ABC1234, AB123A1234, AB12ABC1234 OR
DFXXXXXX For Defence Vehicle
TRXXXXXX For Temporary RC
BPXXXXXX For Bhutan
NPXXXXXX For Nepal
How to generate an E-way bill?
As a GST taxpayer in India, we need to generate an E-way bill online for the movement of goods in the same state or outside of the state so we should know how to generate an e-way bill online which is the need in every business for the movement of goods as outward or inward supply.
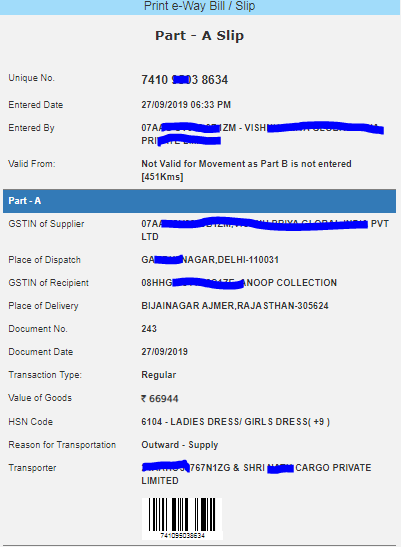
Before initiating a new EWB generation, the user should have the Invoice/Bill/Challan document/details in his hand and he should know the Transporter Id of the transporter, through whom he is going to move the consignment or vehicle details (Part-B) through which the consignment will be moved.
Here we need to follow these steps to issue/ generate an E-way bill online
How to fill E-way bill Part A?
- First step- search in google login e-way bill portal link or ewaybillgst.gov.in
- The second step- log in to the e-way bill portal with your user id or password
- The third step- then go to E-waybill > Generate new> E-way bill entry form
- Then fill e-way bill form by choosing the available option according to your supply type
- choose supply type> sub type > document type> document no> document date> transaction type> enter GSTIN no of consignor or consignee and the third party or fourth party detail if supply from third place or supply to the fourth place> product name> description> HSN code> quantity> unit> taxable value> GST tax rate> cess if applicable> transport name> transport id/GSTIN> distance in km>and submit if truck no is not available.
- After submitting you have completed your Part A

- Now you can send your package with e-way bill part A or invoice to the transporter.
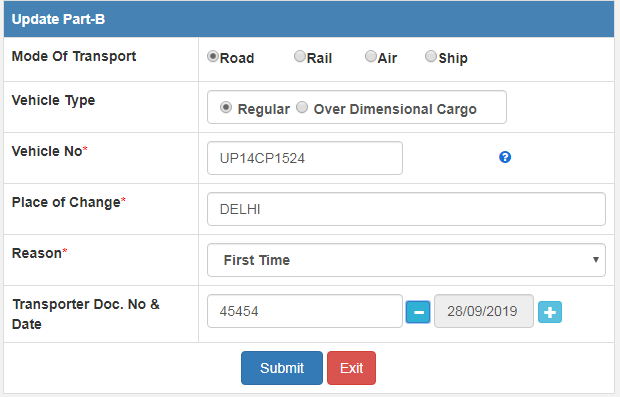
How to Fill E-way bill Part B?
- Then the transporter will complete PART B by login their E-way bill portal online
- Part b needs to update through the consignor or transporter as per choice.
- For completing Part b just you will have to choose the option E-waybill> Update Part B/ Vehicle>
- Then enter E-way bill no> and fill in the detail of transporter> mode of transport( Road, Rail, Air, Ship)> vehicle type (Regular, over-dimensional cargo)> enter vehicle no> place of change, if required> Reason (first time or any other if applicable)> transporter document no & date (a bilty no, railway receipt no, Airways bill no, bill of landing no)> enter date
- Then click on submit.
- Finally, your e-way bill is complete.
- Now the transporter will send the consignment to the consignee by any vehicle with an e-way bill, Invoice, challan, etc.

How to print the E-way bill from the portal?
If you need a printout of an E-way bill generated by you then there is a simple process and ways:
- The first way to print the E-way bill at the time of completion of Part A > submit and Get print
- And the second way to print is when the transporter updates the E-way bill and you are to get a print of an e-way bill for your record then use these steps
- Go to E-waybill> Print EWB> Enter the e-way bill no> submit and take Print out.
How to cancel the generated new E-way bill?
There is a simple process to cancel the E-way bill on the portal just you will have to log in E-way bill portal and will have to go to the option available for the cancelation of the E-way bill as
- Firstly, Go to the E-waybill> Cancel> Enter the e-way bill no
- Then choose cancel reason (Duplicate, Order canceled, Data entry mistake, and other)
- Enter any remark
- Submit with the cancel button
- And your E-way bill will get canceled
- Completed E-way bill can be canceled in 24 hours after that no cancellation
- Part A can be canceled at any time and it will be dismissed within 15 days if Part B is entered.
How to Update E-way bill Transporter?
Above all, sometimes your transporter will refuse to move your packages after all you have generated an e-way bill for that transporter now the question is “can you change your transporter”.
So, yes you can change the transporter by updating the transporter GSTIN online
Here are the steps to update the E-way bill transporter online
- Firstly go to E-way bill > Update EWB transporter> Enter E-way bill No> will show all detail of E-way bill > Enter new transporter GSTIN no in Transport id (option)> Enter Tab button ( for showing the name of the transporter) > and, submit>
- Further, get the new printout of the updated E-way bill
- And then sent the consignment through the new updated E-way bill
How to extend the validity of an E-way bill?
The provision has been provided to the taxpayer to extend the validity of the E-way bill if the consignment is delayed and cannot reach the destination before the expiry of the validity of the e-way bill.
The user can extend the e-way Bill eight hours before or within eight hours after the existing validity time of EWB.
The present transporter of the e-way bill can only extend the validity.
In short, these are the steps to extend the validity
- Firstly login to the E-way bill portal after that go to E-waybill> Extend validity> Enter E-way bill no> choose Yes option> select the reason> select option of ‘in movement or in transit>
- In Movement On selection of “In Movement” the system will prompt the user to select the “Mode” and “Vehicle details”.
- In Transit On selection of “In Transit”, the user needs to select the “Transit type” i.e. On Road, Warehouse, or Others followed by the Address details of the transit place.
Subsequently, the user has to update Transportation Details-Part B as shown in the above figure including the approximate remaining distance to be covered from the present place of a conveyance carrying the consignment to the destination.
On click of the “Submit” button and subsequent validation of entered details by the system, the validity of the EWB is extended depending upon the distance to travel as per the defined EWB rules.
- How to login Udyam Registration Portal?
- Delhi EWS/DG Admission for 24-25, Eligibility, Dates
- Open cheque meaning, example, fillup, image & benefits
- Post dated cheque example, meaning, fillup & benefits
- Ante dated cheque meaning, example, filling & benefits

An Accountant, GSTP, GST blogger, Website Creator, SEO Builder & Co-founder of the website https://gstportalindia.in for the help of GST Taxpayers of India. Having a perfect accounting experience of more than 10 years in a Private Ltd Company.
